Vue.js 源码剖析-模板编译和组件化
模板编译
- 模板编译的主要目的是将模板(
template)转换为渲染函数(render)
<div>
<h1 @click="handler">Title</h1>
<p>some content</p>
</div>- 渲染函数
- h()函数的作用最终回到用vm.$createElmnent()生成VNode
render(h) {
return h('div', [
h('h1', { on: { click: this.handler } }, 'title'),
h('p', 'some content')
])
}- 模板编译的作用
- Vue2.x使用VNode描述视图以及各种交互,用户自己编写VNode比较复杂
- 用户只需要编写类似HTML的代码(Vue模板),通过编译器将模板转换为返回VNode的
render函数 - .vue文件会被webpack在构建过程中转换成
render函数。webpack本身不支持把模板编译成render函数,其内部使用vue-loader进行操作。 - 根据编译时间,可以把编译过程分为运行时编译和构建时编译
- 运行时编译
- 前提:必须使用完整版的Vue,因为完整版的Vue才带编译器。在项目运行的过程中把模板编译成
render函数 - 缺点:Vue体积大,运行速度慢
- 前提:必须使用完整版的Vue,因为完整版的Vue才带编译器。在项目运行的过程中把模板编译成
- 构建时编译
- vue-cli创建的项目,默认加载的是运行版本的Vue,不带编译器,体积小
- 优点:
webpack+vue-loader把模板编译成render函数,加载运行时版本的vue体积小,不需要额外的操作,所以速度快
- 运行时编译
体验模板编译的结果
带编译器版本的Vue.js,使用
template或el的方式设置模板<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>compile</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1>Vue<span>模板编译过程</span></h1> <p>{{ msg }}</p> <comp @myclick="handler"></comp> </div> <script src="../../dist/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component('comp', { template: '<div>I am a comp</div>' }) const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { msg: 'Hello compiler' }, methods: { handler () { console.log('test') } } }) console.log(vm.$options.render) </script> </body> </html>编译后
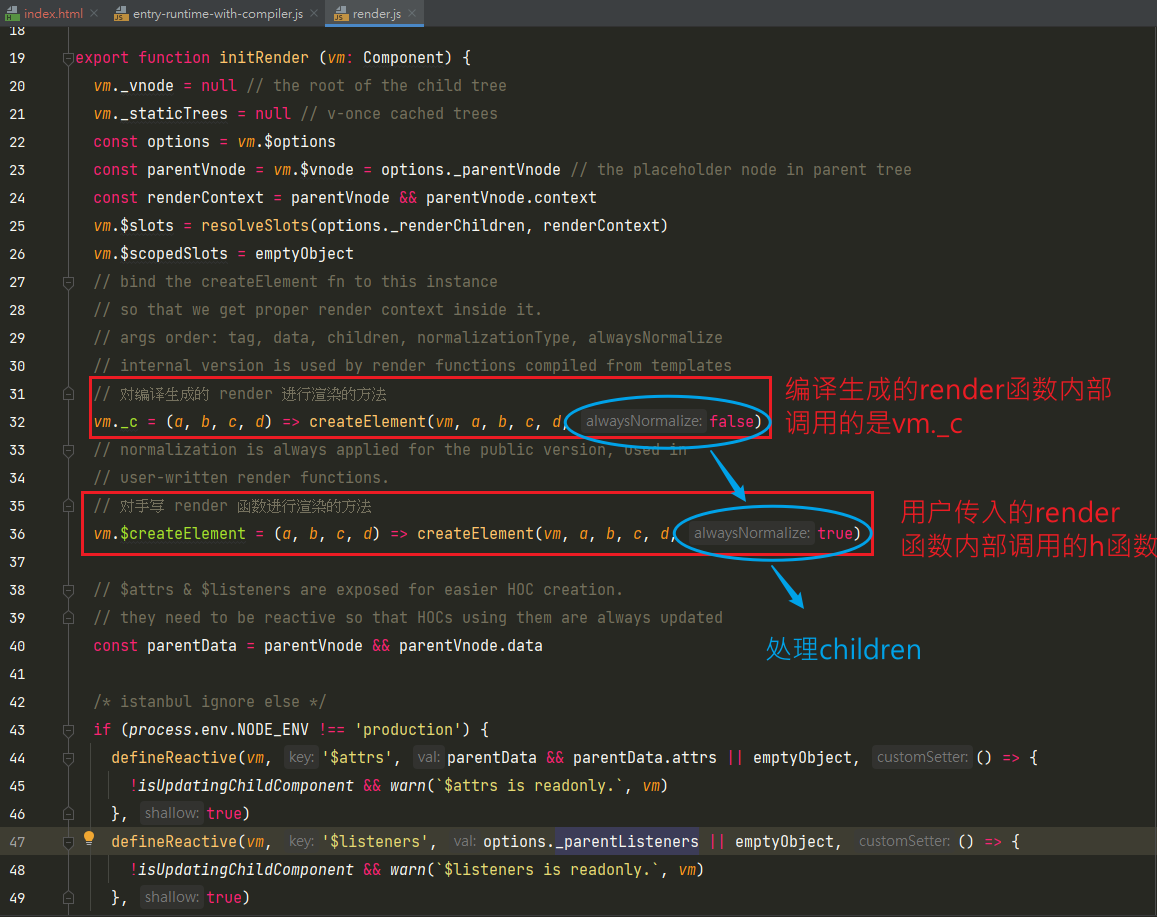
render输出的结果(function anonymous() { // with的作用是在使用with的代码块中,使用this时可以省略this。this._v/this._c...... with (this) { return _c( "div", {attrs: {id: "app"}}, [ _m(0), // renderStatic,对应模板的h1标签 _v(" "), // createTextVNode 创建h1标签与p标签之间的空白文本节点 _c("p", [_v(_s(msg))]), // createElement(createTextVNode(toString(msg))) _v(" "), // createTextVNode(" ") _c("comp", {on: {myclick: handler}}), // createElement() ], 1 // 如果children为二维数组,则将其拍平为一维数组 ); } });_c是createElement()方法,定义的位置instance/render.js中
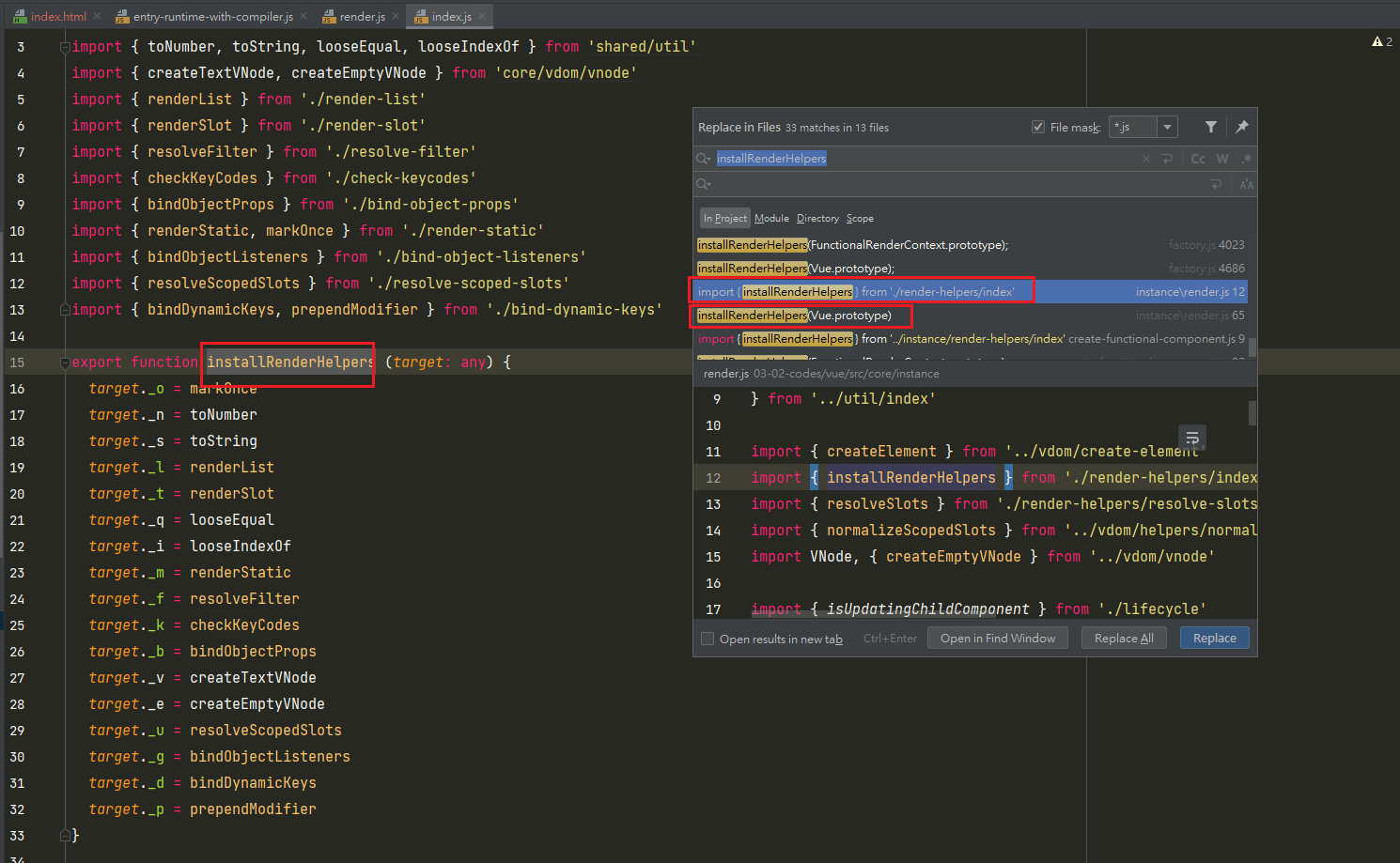
相关的渲染函数(_开头的方法定义),在instance/render-helps/index.js
installRenderHelpers(target:any)
export function installRenderHelpers (target: any) { target._o = markOnce target._n = toNumber target._s = toString // toString函数 target._l = renderList target._t = renderSlot target._q = looseEqual target._i = looseIndexOf target._m = renderStatic // 处理静态内容 target._f = resolveFilter target._k = checkKeyCodes target._b = bindObjectProps target._v = createTextVNode // 创建文本VNode节点 target._e = createEmptyVNode target._u = resolveScopedSlots target._g = bindObjectListeners target._d = bindDynamicKeys target._p = prependModifier }target._v = createTextVNode–>src/core/vdom/vnode.jsexport function createTextVNode (val: string | number) { return new VNode(undefined, undefined, undefined, String(val)) }target._s = toString–>src/shared/util.jsexport function toString (val: any): string { return val == null ? '' : Array.isArray(val) || (isPlainObject(val) && val.toString === _toString) ? JSON.stringify(val, null, 2) : String(val) }target._m = renderStatic–>instance/render-helps/render-static.jsexport function renderStatic ( index: number, isInFor: boolean ): VNode | Array<VNode> { const cached = this._staticTrees || (this._staticTrees = []) let tree = cached[index] // if has already-rendered static tree and not inside v-for, // we can reuse the same tree. if (tree && !isInFor) { return tree } // otherwise, render a fresh tree. tree = cached[index] = this.$options.staticRenderFns[index].call( this._renderProxy, null, this // for render fns generated for functional component templates ) markStatic(tree, `__static__${index}`, false) return tree }
把
template转换成render的入口src/platform/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js,在Vue.prototype.$mount方法中// 保留 Vue 实例的 $mount 方法 const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, // 非ssr情况下为 false,ssr 时候为true hydrating?: boolean ): Component { // 获取 el 对象 el = el && query(el) /* istanbul ignore if */ // el 不能是 body 或者 html if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.` ) return this } const options = this.$options // resolve template/el and convert to render function // 把 template/el 转换成 render 函数 if (!options.render) { let template = options.template // 如果模板存在 if (template) { if (typeof template === 'string') { // 如果模板是 id 选择器 if (template.charAt(0) === '#') { // 获取对应的 DOM 对象的 innerHTML template = idToTemplate(template) /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) { warn( `Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`, this ) } } } else if (template.nodeType) { // 如果模板是元素,返回元素的 innerHTML template = template.innerHTML } else { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { warn('invalid template option:' + template, this) } // 否则返回当前实例 return this } } else if (el) { // 如果没有 template,获取el的 outerHTML 作为模板 template = getOuterHTML(el) } if (template) { /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile') } // 把 template 转换成 render 函数 const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, { outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production', shouldDecodeNewlines, shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref, delimiters: options.delimiters, comments: options.comments }, this) options.render = render options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile end') measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end') } } } // 调用 mount 方法,渲染 DOM return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) }
Vue Template Explorer
- vue-template-explorer
- Vue2.6把模板编译成render函数的工具

- vue-next-template-explorer
- Vue3.0beta把模板编译成render函数的工具

通过观察编译生成的render函数,可以发现在Vue2的模板的时候,标签内的文本内容尽量不要添加空白的文本内容(空格、换行等)。而Vue3则没有要求,Vue3编译后的render函数已经去除了标签内多余的空白。
模板编译过程
- 解析、优化、生成
编译的入口
src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( …… // 把 template 转换成 render 函数 const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, { outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production', shouldDecodeNewlines, shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref, delimiters: options.delimiters, comments: options.comments }, this) options.render = render options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns …… )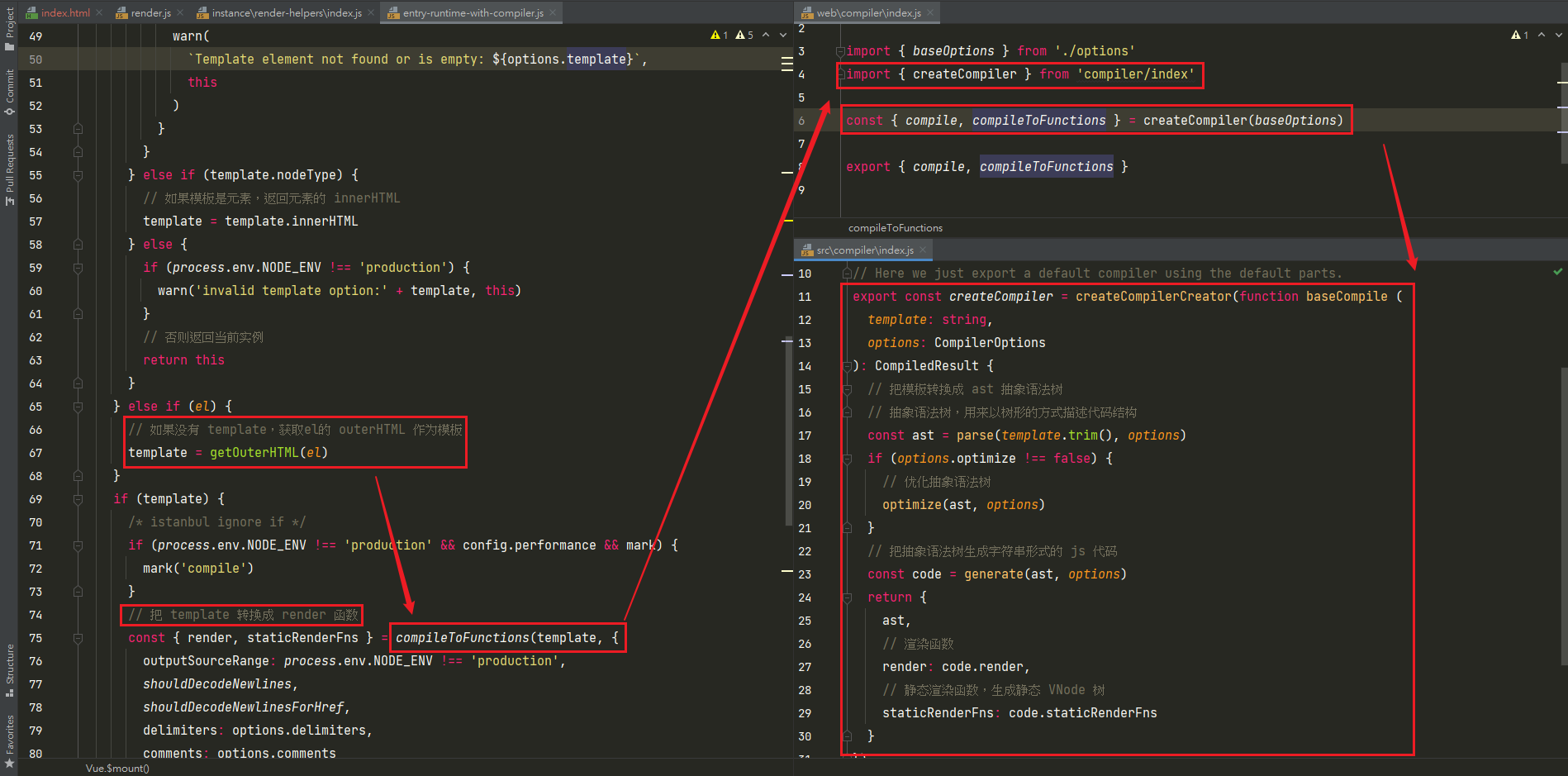
调试
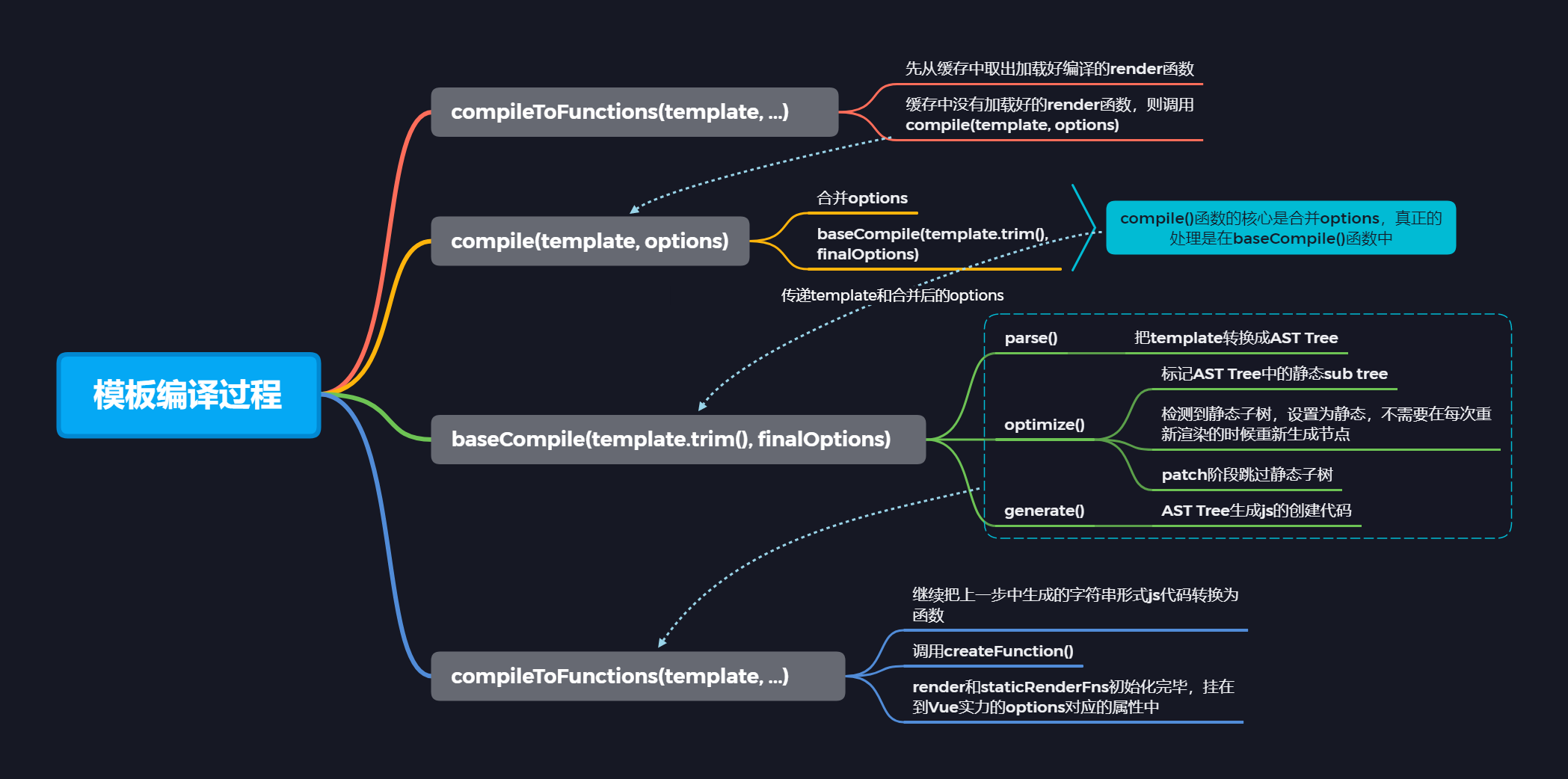
compileToFunctions()执行过程,生成渲染函数的过程compileToFunctions:src/compiler/to-function.jscompile(template, options): src/compiler/create-compiler.jsbaseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions): src/compiler/index.js
render,staticRenderFns由compileToFunction()函数返回compileToFunctions()函数由createCompiler()函数返回createCompiler函数传入参数baseOptions- baseOptions中导出options
modules:模块klassstylemodel- 与
v-if一起使用的v-model
- 与
directives:指令model:处理v-modeltext:处理v-texthtml:处理v-html
isPreTag:是否是Pre标签isUnaryTag:是否是一元标签(自闭和标签)mustUseProp:是否要放入el.prop中canBeLeftOpenTagisReservedTag:是否是HTML中保留标签getTagNamespase- …
- baseOptions中导出options
createCompiler函数由createCompilerCreater()函数返回createCompilerCreater()函数传入参数为baseCompile()函数baseCompile()函数内容- 把模板转换成ast抽象语法树
- 抽象语法树,用来以树形的方式描述代码结构
- 优化抽象语法树
- 吧抽象语法树生成字符串形式的js代码
- 返回
ast对象- 渲染函数
render - 静态渲染函数,生成静态VNode树:
staticRenderFns
createCompilerCreater()函数内容- 返回
createCompiler()函数createCompiler()函数内容- 定义
compile函数,接受参数:模板template、用户传入的optionscompile函数中会把createCompiler函数中和平台相关的baseOptions与用户传入的options合并- 然后调用
baseCompile()函数,把合并后的选项参数options传递给它 - 最终返回compile函数和
compileToFunctions- compileToFunctions()通过
createCompileToFunctionFn()函数返回 createCompileToFunctionFn()函数就是模板编译的入口函数
- compileToFunctions()通过
- 定义
- 返回
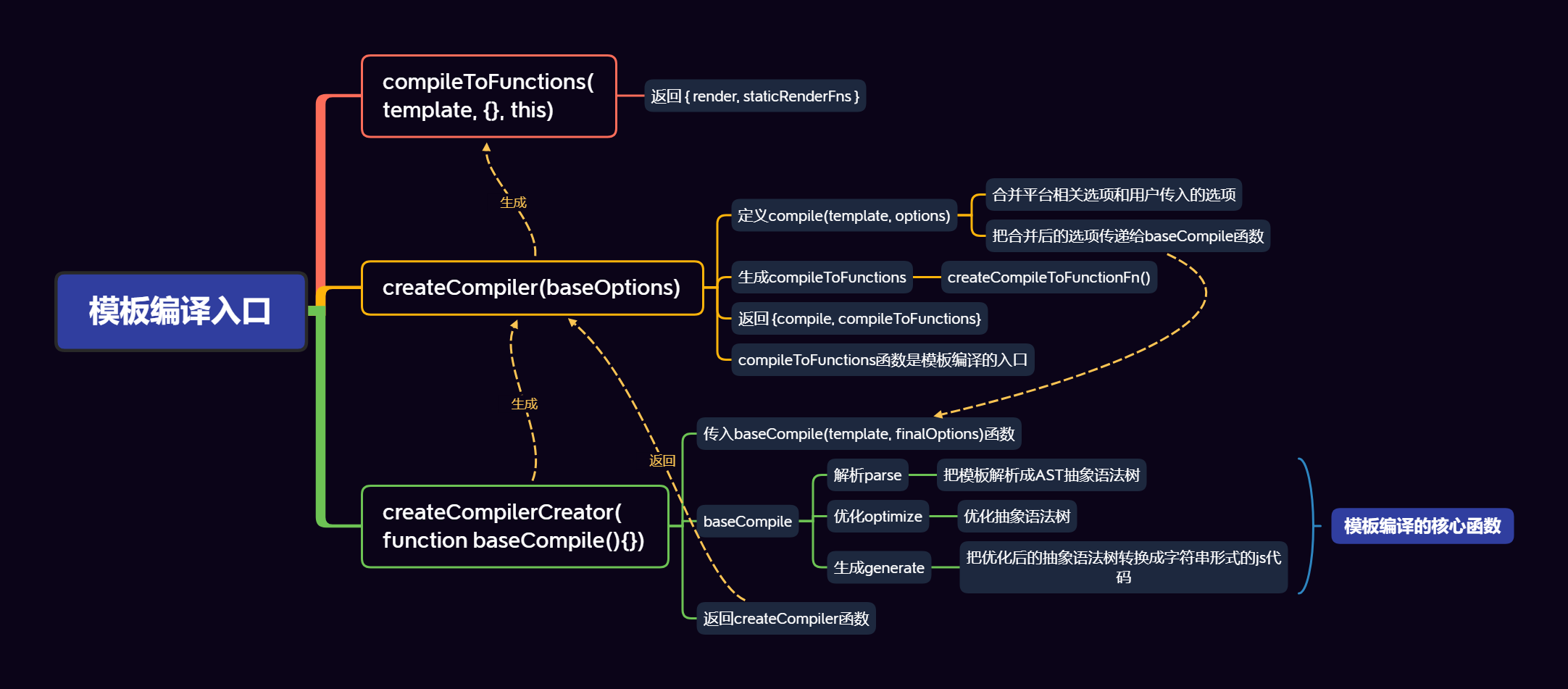
compileToFunctions
createCompilerCreator()
参数:
baseCompile()函数返回:createCompiler()函数
createCompiler()函数中定义了compile()函数返回:
compileToFunctionscompileToFunctions由函数createCompileToFunctionFn()函数返回export function createCompileToFunctionFn (compile: Function): Function { const cache = Object.create(null) return function compileToFunctions ( template: string, options?: CompilerOptions, vm?: Component ): CompiledFunctionResult { // 合并options options = extend({}, options) const warn = options.warn || baseWarn delete options.warn /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { // detect possible CSP restriction try { new Function('return 1') } catch (e) { if (e.toString().match(/unsafe-eval|CSP/)) { warn( 'It seems you are using the standalone build of Vue.js in an ' + 'environment with Content Security Policy that prohibits unsafe-eval. ' + 'The template compiler cannot work in this environment. Consider ' + 'relaxing the policy to allow unsafe-eval or pre-compiling your ' + 'templates into render functions.' ) } } } // check cache // 1. 读取缓存中的 CompiledFunctionResult 对象,如果有直接返回 // 时间换空间,key为模板的内容 // delimiters为插值表达式的符号{{}} const key = options.delimiters ? String(options.delimiters) + template : template if (cache[key]) { return cache[key] } // compile // 2. 把模板编译为编译对象(render, staticRenderFns),字符串形式的js代码3 // render中含有两个属性errors和tips const compiled = compile(template, options) // check compilation errors/tips if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { if (compiled.errors && compiled.errors.length) { if (options.outputSourceRange) { compiled.errors.forEach(e => { warn( `Error compiling template:\n\n${e.msg}\n\n` + generateCodeFrame(template, e.start, e.end), vm ) }) } else { warn( `Error compiling template:\n\n${template}\n\n` + compiled.errors.map(e => `- ${e}`).join('\n') + '\n', vm ) } } if (compiled.tips && compiled.tips.length) { if (options.outputSourceRange) { compiled.tips.forEach(e => tip(e.msg, vm)) } else { compiled.tips.forEach(msg => tip(msg, vm)) } } } // turn code into functions const res = {} const fnGenErrors = [] // 3. 把字符串形式的js代码转换成js方法 res.render = createFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors) res.staticRenderFns = compiled.staticRenderFns.map(code => { return createFunction(code, fnGenErrors) }) // check function generation errors. // this should only happen if there is a bug in the compiler itself. // mostly for codegen development use /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { if ((!compiled.errors || !compiled.errors.length) && fnGenErrors.length) { warn( `Failed to generate render function:\n\n` + fnGenErrors.map(({ err, code }) => `${err.toString()} in\n\n${code}\n`).join('\n'), vm ) } } // 4. 缓存并返回res对象(render, staticRenderFns方法) return (cache[key] = res) } }函数核心:
- 先去找缓存中编译的结果
- 如果有的话直接返回
- 如果没有的话开始编译(
compile()) - 并且把编译后的字符串的js代码转换成函数的形式(
createFunction()) - 缓存并且返回
compile
- 参数
- template模板
- options选项(调用compileToFunctions时传入的选项,可以认为时用户传入的选项)
function compile (
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
// 合并options
const finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions)
// 存储编译过程中出现的错误和一些信息
const errors = []
const tips = []
let warn = (msg, range, tip) => {
(tip ? tips : errors).push(msg)
}
if (options) {
// 开始合并baseOptions和options
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && options.outputSourceRange) {
// $flow-disable-line
const leadingSpaceLength = template.match(/^\s*/)[0].length
warn = (msg, range, tip) => {
const data: WarningMessage = { msg }
if (range) {
if (range.start != null) {
data.start = range.start + leadingSpaceLength
}
if (range.end != null) {
data.end = range.end + leadingSpaceLength
}
}
(tip ? tips : errors).push(data)
}
}
// merge custom modules
if (options.modules) {
finalOptions.modules =
(baseOptions.modules || []).concat(options.modules)
}
// merge custom directives
if (options.directives) {
finalOptions.directives = extend(
Object.create(baseOptions.directives || null),
options.directives
)
}
// copy other options
for (const key in options) {
if (key !== 'modules' && key !== 'directives') {
finalOptions[key] = options[key]
}
}
}
finalOptions.warn = warn
// 调用baseCompile()模板编译的核心函数
// compiled为对象,两个成员render和staticRender,此时的render中存储的是字符串形式的代码,在入口函数中调用compileToFunctions中把字符串形式的js代码转换成函数
const compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
detectErrors(compiled.ast, warn)
}
compiled.errors = errors
compiled.tips = tips
return compiled
}核心作用:
- 合并选项
- 调用baseCompile()进行编译
- 记录错误
- 返回编译好的对象
baseCompile-AST
baseCompile是模板编译的核心函数,主要做了三件事:
- 把模板转换成ast抽象语法树
- 优化抽象语法树
- 把抽象语法树生成字符串形式的 js 代码
export const createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
// 把模板转换成 ast 抽象语法树
// 抽象语法树,用来以树形的方式描述代码结构
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options)
if (options.optimize !== false) {
// 优化抽象语法树
optimize(ast, options)
}
// 把抽象语法树生成字符串形式的 js 代码
const code = generate(ast, options)
return {
ast,
// 渲染函数
render: code.render,
// 静态渲染函数,生成静态 VNode 树
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
}
})解析-parse
parse整体过程比较复杂,研究的投入与收获不成正比,这里简单介绍
什么抽象语法树
- 抽象语法树简称AST(Abstract Syntax Tree)
- 使用对象的形式描述树形的代码结构
- 此处的抽象语法树是用来描述树形结构的HTML字符串
为什么要使用抽象语法树
模板字符串转换成AST后,可以通过AST对模板做优化处理
标记模板中的静态内容,在patch的时候直接跳过静态内容
在patch的过程中,静态内容不需要对比和重新渲染
解释器将模板解析为抽象语法树AST,只有将模板解析成AST后,才能给予它做优化或生成代码字符串
src/compiler/index.js
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options) // src/compiler/parser/index.js parse()
查看得到的AST Tree

结构化指令的处理
v-if最终生成单元表达式
// src/compiler/parser/index.js // structural directives // 结构化的指令 // v-for processFor(element) processIf(element) processOnce(element) // src\compiler\codegen\index.js export function genIf ( el: any, state: CodegenState, altGen?: Function, altEmpty?: string ): string { el.ifProcessed = true // avoid recursion return genIfConditions(el.ifConditions.slice(), state, altGen, altEmpty) } // 最终调用 genIfConditions 生成三元表达式v-if最终编译的结果
ƒ anonymous( ) { with(this){ return _c('div',{attrs:{"id":"app"}},[ _m(0), _v(" "), (msg)?_c('p',[_v(_s(msg))]):_e(),_v(" "), _c('comp',{on:{"myclick":onMyClick}}) ],1) } }v-if/v-for结构化指令只能在编译阶段处理,如果我们要在render函数处理条件或者循环只能使用js中deif和for
Vue.component('comp', { data: () { return { msg: 'my comp' } }, render (h) { if (this.msg) { return h('div', this.msg) } return h('div', 'bar') } })
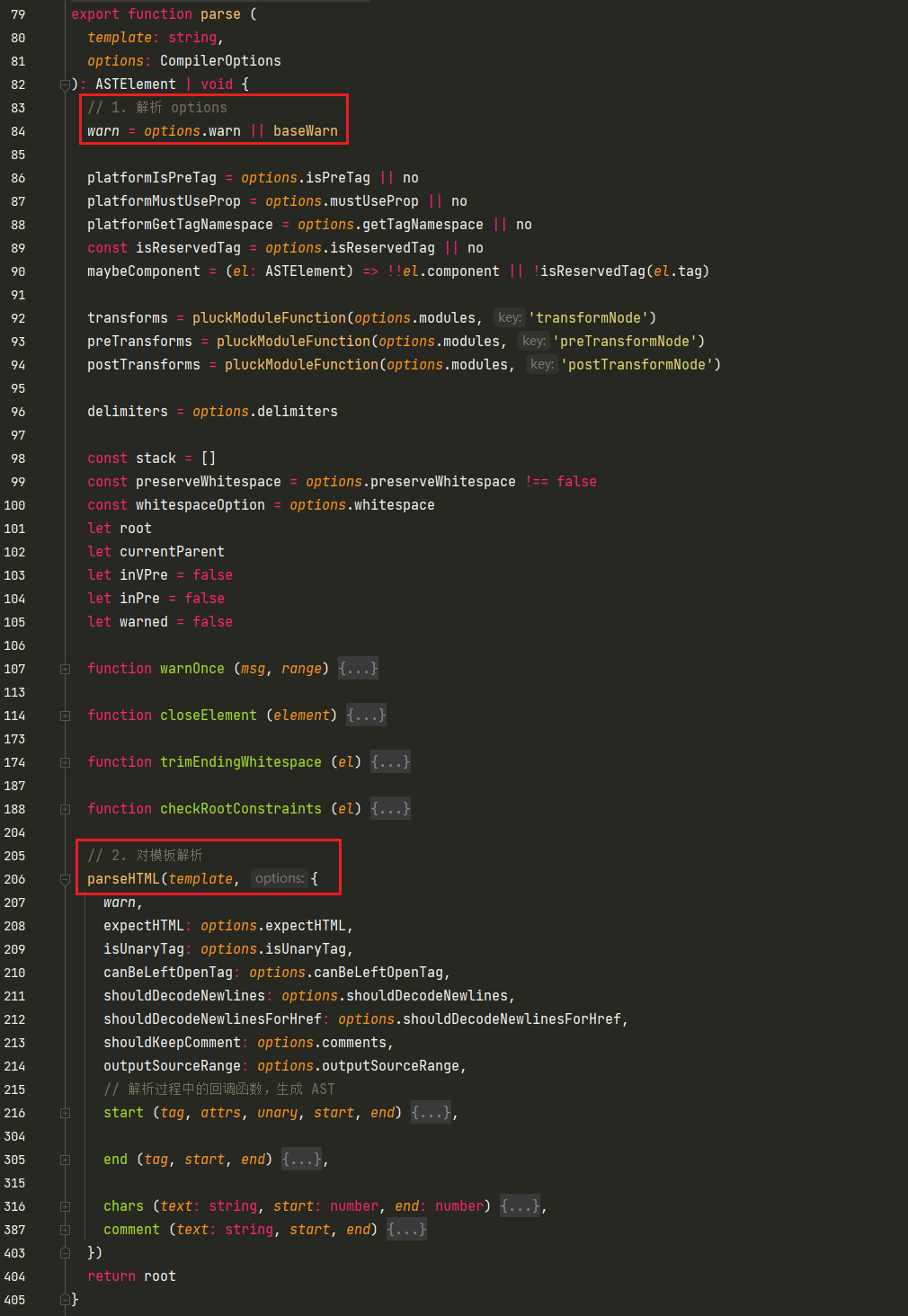
parseHTML

parse整体过程
- parse函数内容处理的过程中会依次去遍历HTML模板字符串,把HTML模板字符串转换成AST对象(普通对象)。HTML中属性和指令都会记录在AST对象中的相应属性上
优化-optimize
优化抽象语法树,检查子节点是否是纯静态节点
一旦检测到纯静态节点,例如:
hello整体是静态节点
永远不会更改的节点
- 提升为敞亮,重新渲染的时候不再重新创建节点
- 在patch的时候跳过静态子树
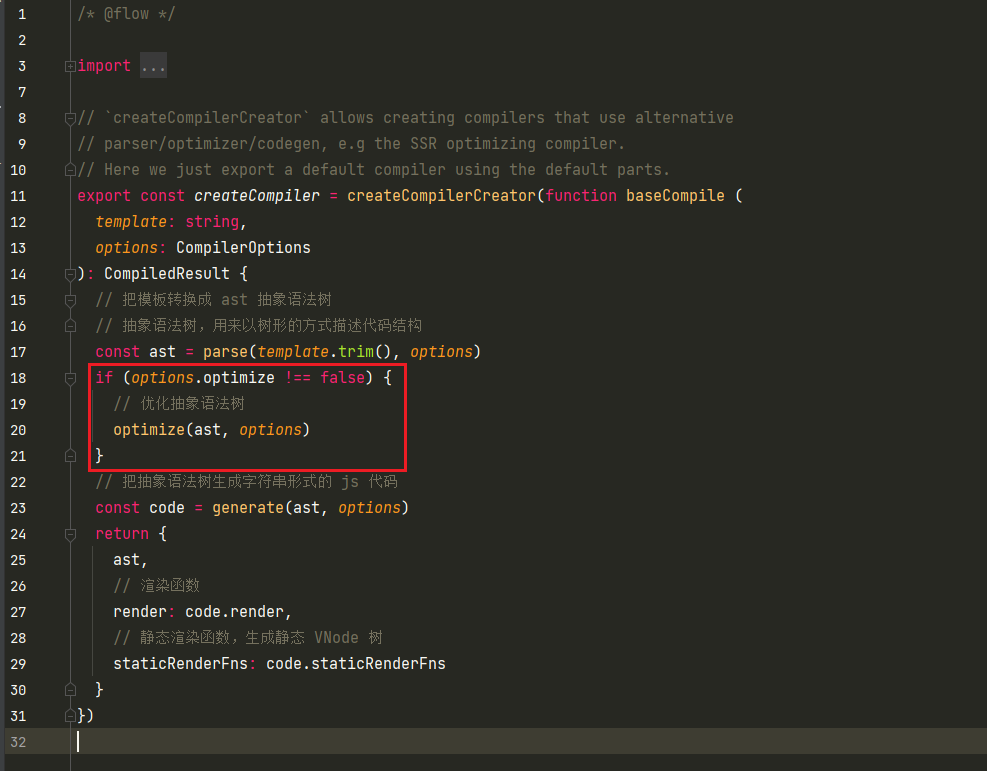
/**
* Goal of the optimizer: walk the generated template AST tree
* and detect sub-trees that are purely static, i.e. parts of
* the DOM that never needs to change.
*
* Once we detect these sub-trees, we can:
*
* 1. Hoist them into constants, so that we no longer need to
* create fresh nodes for them on each re-render;
* 2. Completely skip them in the patching process.
*/
export function optimize (root: ?ASTElement, options: CompilerOptions) {
if (!root) return
isStaticKey = genStaticKeysCached(options.staticKeys || '')
isPlatformReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no
// first pass: mark all non-static nodes.
// 标记静态节点
markStatic(root)
// second pass: mark static roots.
// 标记静态根节点
markStaticRoots(root, false)
}
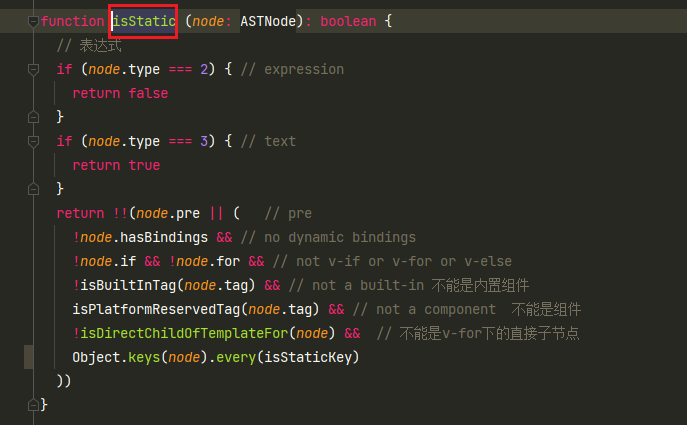

optimize中只是去标记AST对象及其子对象的静态节点和静态根节点。静态根节点指的是:标签中包含子标签并且没有动态内容,也即是里面为纯文本内容。如果标签中只包含纯文本内容没有子标签,Vue中是不会对它做优化的,因为优化的成本大于收益。
生成-generate
src/compiler/index.js
const code = generate(ast, options)src/compiler/codegen/index.js
export function generate ( ast: ASTElement | void, options: CompilerOptions ): CodegenResult { // 代码创建过程中生成的state对象 const state = new CodegenState(options) const code = ast ? genElement(ast, state) : '_c("div")' return { render: `with(this){return ${code}}`, staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns } }src/compiler/to-function.js
function createFunction (code, errors) { try { return new Function(code) } catch (err) { errors.push({ err, code }) return noop } }
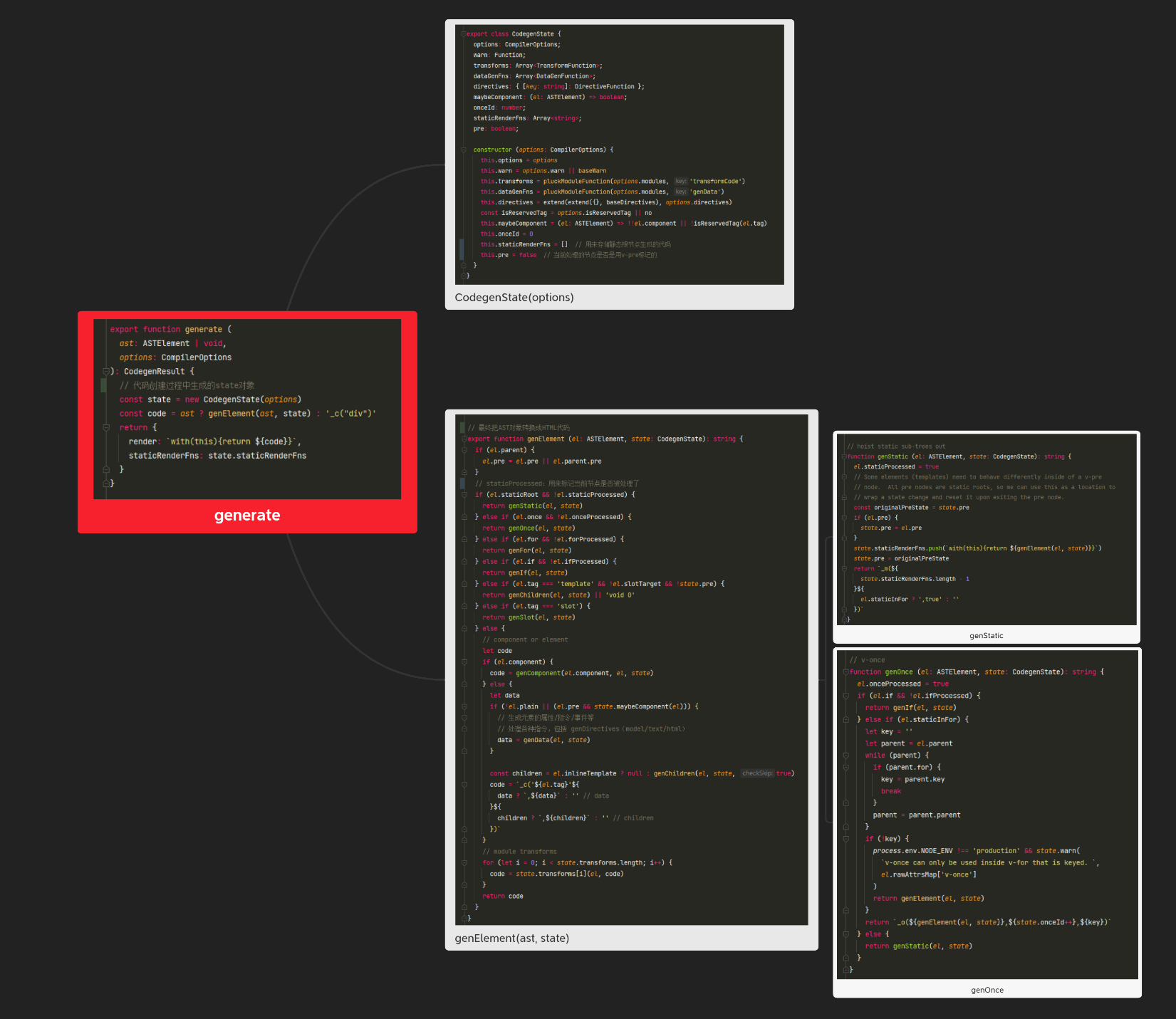
模板编译完整过程
通过观察模板编译的源代码,我们可以了解到:
- 模板编译的过程中会标记静态根节点,对静态根节点进行优化处理,重新渲染时不需要再处理静态根节点,因为它的内容不会改变。
- 再模板中不要写一些无意义的换行、空白字符,否则生成对应的AST对象会保留这些空白和换行,它们都会被存储到内存中。而这些空白和换行对浏览器渲染来说是没有任何意义的
组件化机制
- 组件化可以让我们方便的把页面拆分成多个可重用的组件
- 组件是独立的,系统内可重用,组件之间可以嵌套
- 有了组件就可以像搭积木一样开发网页
- 下面我们将从远吗的角度来分析Vue’zuijanneiburuhegongzuo
- 组件实例的创建过程是从上而下
- 组件实例的挂载过程是从下而上
组件声明
复习全局组件的定义方式
<div id="app"></div> <script> const Comp = Vue.component('comp', { template: '<div>Hello Component</div>' }) const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', render (h) { return h(Comp) } }) </script>Vue.component()入口创建组件的构造函数,挂载到Vue实例的
vm.options.component.componentName = Ctor// src/core/global-api/index.js // 注册 Vue.directive()、 Vue.component()、Vue.filter() initAssetRegisters(Vue)// src/core/global-api/assets.js /* @flow */ import { ASSET_TYPES } from 'shared/constants' import { isPlainObject, validateComponentName } from '../util/index' export function initAssetRegisters (Vue: GlobalAPI) { /** * Create asset registration methods. */ // 遍历 ASSET_TYPES 数组,为 Vue 定义相应方法 // ASSET_TYPES 包括了directive、 component、filter ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => { Vue[type] = function ( id: string, definition: Function | Object ): Function | Object | void { if (!definition) { return this.options[type + 's'][id] } else { /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && type === 'component') { validateComponentName(id) } // Vue.component('comp', { template: '' }) if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) { definition.name = definition.name || id // 把组件配置转换为组件的构造函数 definition = this.options._base.extend(definition) } if (type === 'directive' && typeof definition === 'function') { definition = { bind: definition, update: definition } } // 全局注册,存储资源并赋值 // this.options['components']['comp'] = definition this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition return definition } } }) }// src/core/global-api/index.js // this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object // components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios. Vue.options._base = Vue // src/core/global-api/extend.js Vue.extend()
组件构造函数的创建
Vue.extend()
/* @flow */
import { ASSET_TYPES } from 'shared/constants'
import { defineComputed, proxy } from '../instance/state'
import { extend, mergeOptions, validateComponentName } from '../util/index'
export function initExtend (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Each instance constructor, including Vue, has a unique
* cid. This enables us to create wrapped "child
* constructors" for prototypal inheriance and cache them.
*/
Vue.cid = 0
let cid = 1
/**
* Class inheritance
*/
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function {
extendOptions = extendOptions || {}
// Vue 构造函数
const Super = this
const SuperId = Super.cid
// 从缓存中加载组件的构造函数
const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {})
if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) {
return cachedCtors[SuperId]
}
const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.name
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) {
// 如果是开发环境验证组件的名称
validateComponentName(name)
}
const Sub = function VueComponent (options) {
// 调用 _init() 初始化
this._init(options)
}
// 原型继承自 Vue
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
Sub.cid = cid++
// 合并 options
Sub.options = mergeOptions(
Super.options,
extendOptions
)
Sub['super'] = Super
// For props and computed properties, we define the proxy getters on
// the Vue instances at extension time, on the extended prototype. This
// avoids Object.defineProperty calls for each instance created.
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub)
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub)
}
// 继承Vue原型对象上的属性
// allow further extension/mixin/plugin usage
Sub.extend = Super.extend
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin
Sub.use = Super.use
// create asset registers, so extended classes
// can have their private assets too.
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type]
})
// enable recursive self-lookup
// 把组件构造构造函数保存到 Ctor.options.components.comp = Ctor
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
// keep a reference to the super options at extension time.
// later at instantiation we can check if Super's options have
// been updated.
Sub.superOptions = Super.options
Sub.extendOptions = extendOptions
Sub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options)
// cache constructor
// 把组件的构造函数缓存到 options._Ctor
cachedCtors[SuperId] = Sub
return Sub
}
}
function initProps (Comp) {
const props = Comp.options.props
for (const key in props) {
proxy(Comp.prototype, `_props`, key)
}
}
function initComputed (Comp) {
const computed = Comp.options.computed
for (const key in computed) {
defineComputed(Comp.prototype, key, computed[key])
}
}调试Vue.component()调用的过程
<div id="app"></div> <script> const Comp = Vue.component('comp', { template: '<div>Hello Component</div>' }) const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', render (h) { return h(Comp) } }) </script>
组件创建和挂载
回顾首次渲染过程
- Vue构造函数 –>调用↓
- this._init() –>调用↓
- this.$mount() –>调用↓
- mountCompunent() –>创建↓
- new Watcher() 渲染Watcher –>传入updateComponent()↓
- updateComponent() –>调用↓
- vm._render() -> createElement()
- vm._update()

组件VNode的创建过程

- 创建根组件,首次_render()时,会得到整棵树的VNode结构
- 整体流程:
new Vue() --> $mount() --> vm._render() --> createElement() --> createComponent() - 创建组件的VNode,初始化组件的hook钩子函数
// 1._createElement()中调用了createComponent()
// src/core/vdom/create-element.js
else if ((!data || !data.pre) &&
isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {
// 查找自定义组件构造函数的声明
// 根据 Ctor 创建组件的 VNode
// component
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
}// 2.createComponent()中调用创建自定义组件对应的VNode
// src/core/vdom/create-component.js
export function createComponent (
Ctor: Class<Component> | Function | Object | void,
data: ?VNodeData,
context: Component,
children: ?Array<VNode>,
tag?: string
): VNode | Array<VNode> | void {
if (isUndef(Ctor)) {
return
}
...
// install component management hooks onto the placeholder node
// 安装组件的钩子函数 init/prepatch/insert/destroy
// 准备好了 data.hook 中的钩子函数
installComponentHooks(data)
// return a placeholder vnode
const name = Ctor.options.name || tag
// 创建自定义组件的 VNode,设置自定义组件的名字
// 记录this.componentOptions = componentOptions
const vnode = new VNode(
`vue-component-${Ctor.cid}${name ? `-${name}` : ''}`,
data, undefined, undefined, undefined, context,
{ Ctor, propsData, listeners, tag, children },
asyncFactory
)
return vnode
}// 3.installComponentHooks()初始化组件的data.hook
function installComponentHooks (data: VNodeData) {
const hooks = data.hook || (data.hook = {})
// 用户可以传递自定义钩子函数
// 把用户传入的自定义钩子函数和 componentVNodeHooks 中预定义的钩子函数合并
for (let i = 0; i < hooksToMerge.length; i++) {
const key = hooksToMerge[i]
const existing = hooks[key]
const toMerge = componentVNodeHooks[key]
if (existing !== toMerge && !(existing && existing._merged)) {
hooks[key] = existing ? mergeHook(toMerge, existing) : toMerge
}
}
}// 4.钩子函数定义的位置(init()钩子函数中创建组件的实例)
// inline hooks to be invoked on component VNodes during patch
const componentVNodeHooks = {
init (vnode: VNodeWithData, hydrating: boolean): ?boolean {
if (
vnode.componentInstance &&
!vnode.componentInstance._isDestroyed &&
vnode.data.keepAlive
) {
// kept-alive components, treat as a patch
const mountedNode: any = vnode // work around flow
componentVNodeHooks.prepatch(mountedNode, mountedNode)
} else {
// 创建组建的实例挂载到vnode.componentInstance
const child = vnode.componentInstance = createComponentInstanceForVnode(
vnode,
activeInstance
)
child.$mount(hydrating ? vnode.elm : undefined, hydrating)
}
},
prepatch (oldVnode: MountedComponentVNode, vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {...},
insert (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {...},
destroy (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {...}// 5.创建组件实例的位置,由自定义组件的init()钩子方法调用
export function createComponentInstanceForVnode (
vnode: any, // we know it's MountedComponentVNode but flow doesn't
parent: any, // activeInstance in lifecycle state
): Component {
const options: InternalComponentOptions = {
_isComponent: true,
_parentVnode: vnode,
parent
}
// check inline-template render functions
// 获取 inline-template
// <comp inline-template> xxxx </comp>
const inlineTemplate = vnode.data.inlineTemplate
if (isDef(inlineTemplate)) {
options.render = inlineTemplate.render
options.staticRenderFns = inlineTemplate.staticRenderFns
}
// 创建组件实例
return new vnode.componentOptions.Ctor(options)
}- 调试执行过程
组件实例的创建和挂载过程
- Vue._update() –> patch() –> createElm() –> createComponent()
// src/core/vdom/patch.js
// 1.创建组件实例,挂载到真实DOM
function createComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) {
let i = vnode.data
if (isDef(i)) {
const isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive
if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) {
// 调用 init() 方法,创建和挂载组件实例
// init() 的过程中创建好了组件的真实 DOM,挂载到了 vnode.elm 上
i(vnode, false /* hydrating */)
}
// after calling the init hook, if the vnode is a child component
// it should've created a child instance and mounted it. the child
// component also has set the placeholder vnode's elm.
// in that case we can just return the element and be done.
if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) {
// 调用钩子函数(VNode的钩子函数初始化属性/事件/样式等,组件的钩子函数)
initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 把组件对应的 DOM 插入到父元素中
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
if (isTrue(isReactivated)) {
reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)
}
return true
}
}
}// 2.调用钩子函数,设置局部作用于样式
function initComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
if (isDef(vnode.data.pendingInsert)) {
insertedVnodeQueue.push.apply(insertedVnodeQueue, vnode.data.pendingInsert)
vnode.data.pendingInsert = null
}
vnode.elm = vnode.componentInstance.$el
if (isPatchable(vnode)) {
// 调用钩子函数
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 设置局部作用于样式
setScope(vnode)
} else {
// empty component root.
// skip all element-related modules except for ref (#3455)
registerRef(vnode)
// make sure to invoke the insert hook
insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)
}
}// 3.调用钩子函数
function invokeCreateHooks (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
// 调用 VNode 的钩子函数
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, vnode)
}
i = vnode.data.hook // Reuse variable
// 调用组件的钩子函数
if (isDef(i)) {
if (isDef(i.create)) i.create(emptyNode, vnode)
if (isDef(i.insert)) insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)
}
}